高分子多尺度多功能复合是高分子科学的重要问题,决定了体系高性能、多功能程度。发展微尺度加工制备方法学,控制体系形态、组分空间分布及多尺度微结构,实现体系的高性能及智能化。自2000年起,我们面向复杂结构复合颗粒和纳米孔复合膜两种典型复合材料形态,发展了模板合成微加工制备方法,控制宏观形态;通过软物质(高分子凝胶和嵌段共聚物)与其他物质的特殊作用,诱导其定位生长,精确调控多组份多尺度空间分布,系统研究了其物理与化学基本问题。近期,聚焦于Janus功能复合体系合成方法学及界面操控的基本过程,在新材料、能源环境及生物医用方面寻求新策略。
具体研究方向如下:
1、复合中空微球
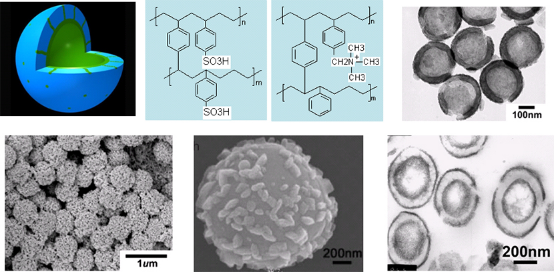
中空微球结合空腔和特定的壳组成,有着广泛实际应用,其微结构控制和规模化制备方法学是关键。我们发展了规模化制备中空微球的普适性新方法,首次提出了模板合成技术结合高分子凝胶软物质诱导功能物质定位生长新概念(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2003,42, 1943;Adv. Funct.Mater.2003,13, 949),充分利用凝胶可渗透性和容易与功能物质复合等特点,制备了壳层厚度与腔体尺寸可连续调节的中空微球,系统研究了高分子凝胶诱导功能物质定位生长的物理与化学问题,指出如催化、络合、静电吸附和离子交换等多重作用决定空间精确定位的生长过程机制,在国际上具有重要影响,已成为广泛使用的方法。该工作的创新性得到了国际材料学家Archer教授的高度认同(Adv.Mater.2008,20, 3987):首次利用高分子凝胶特性制备复合功能中空微球的新概念。上述概念进一步从单个胶体颗粒拓展到三维阵列。相关工作以封面文章发表(Macromol. Mater. Eng.2002, 287, 627)。以多孔中空高分子微球为模板,通过控制物质生长的位点,制备系列新型结构复合微球,同步实现了物质的空间分布和形态精确控制(如单层/双层,表面微结构等)(Angew.Chem. Int. Ed.2005,44, 6727;Adv.Funct. Mater.2005,15, 1523)。该方法具有普适性,高分子凝胶种类/微环境可调,保证其可与宽泛组成的功能物质进行复合,中空球的组成可在更宽范围内调节,为材料微结构控制和诱导优先生长复合功能物质奠定了基础。
2、相变储能微胶囊
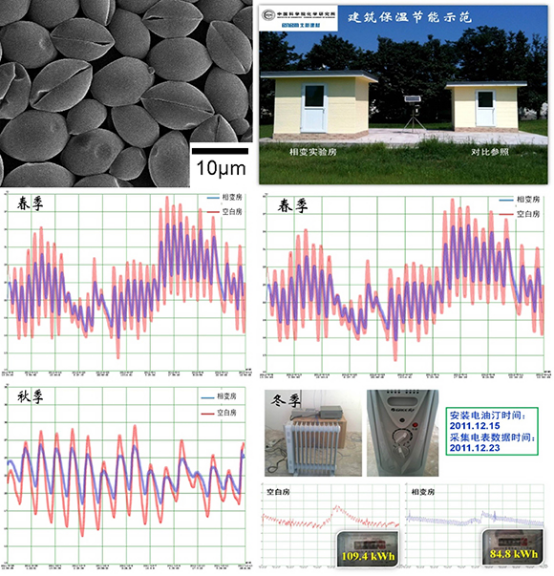
相变材料在窄温度区域发生相变,吸收或释放大量相变潜热,在储能、隔热、智能控温等领域具有重要应用价值。相变材料发生固液相变时,易引起流动、挥发和迁移,严重影响其潜在应用。对相变材料进行微胶囊化是解决该问题基本途径。基于凝胶诱导物质优先生长和聚合诱导相分离的原理,利用乳液聚合技术,建立了批量制备相变微胶囊的方法,壳体材料组成与微胶囊尺寸可调,所制得微胶囊具有焓值保有率高、环保、热稳定性好等特点,制备方法简单、高效,并已实现中试生产。并对于微胶囊进行改性,改善与基体材料的界面相容性、改善相变材料的热输运效率。与北新建材公司合作,成功实现相变微胶囊与石膏板的复合,并建造样板房,连续四年的实测数据显示在春夏秋冬四季中,相变样板房都具有温度波动小、舒适度高、显著节能特点。部分产品已在重要领域中得到实际应用。
3、阻燃防火微胶囊
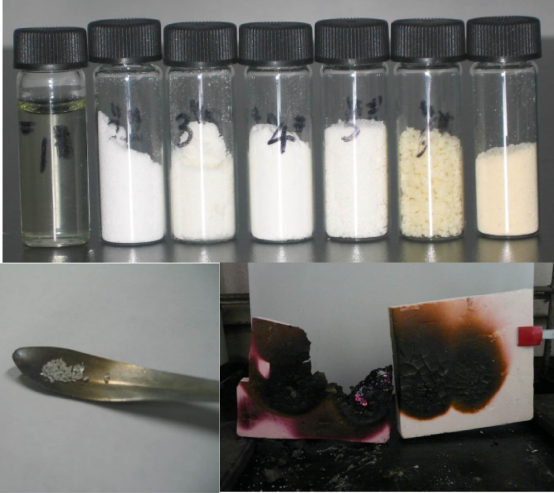

泡沫保温材料在建筑物外墙保温中具有广泛的应用,但其广泛使用带来的一个重要隐患就是消防安全问题。通用阻燃剂在实际使用过程中常常存在诸多问题,例如阻燃剂易吸水失效、与聚合物基体相容性不好、影响聚合物发泡、降低材料机械性能、小分子阻燃剂扩散失效等。阻燃剂微胶囊化是行之有效方法。囊壁隔离阻燃剂与外界环境接触,提高阻燃剂耐久性,改善阻燃效果。我们将高效液体阻燃剂通过包覆形成微胶囊粉末,改善阻燃剂与聚合物材料相容性,减少对复合材料机械性能的不利影响,使用更方便,应用更广泛。微胶囊材料表面进一步改性,以适应不同环境。该阻燃剂为适应不同的应用的防火提供了新思路。
4、Janus复合材料
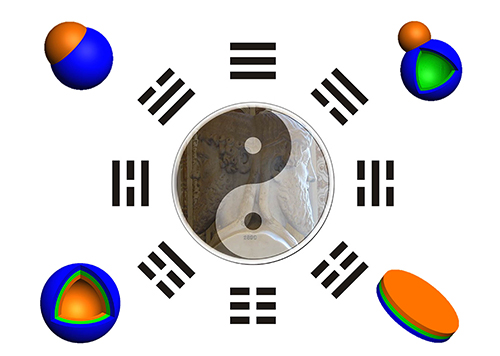
古罗马神Janus的头部具有双面结构,分别朝向过去和未来,与中国的阴阳概念类似,体现了事物的辩证统一。1991年,deGennes在诺贝尔颁奖演讲中,首次借用Janus一词描述同一颗粒两面具有不同化学组成或性质,并预测Janus颗粒类似双亲性分子可在液/液界面自组装具有明确指向,颗粒间的缝隙为物质在两相间传输提供了通道。de Gennes充满启发性的演说引发了Janus颗粒的研究热潮。
Janus材料是物质空间分区和功能集成的典范。进一步将控制复合结构与功能分区拓展到组成和性质分区概念,发展合成不对称的Janus颗粒基本方法,系统研究其性质,为实际应用奠定基础。利用单分散二氧化硅在Pickering乳液油水界面分区特性,结合双相原子转移自由基聚合,制备了有机/无机复合Janus球形胶体,解决了颗粒在液体界面转动难题(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2008,47,3973)。发展了Pickering乳液界面颗粒选区刻蚀并复合方法,制备组成和结构可控的非球形Janus胶体(Chem.Commun.2009, 3871)。进一步发展了乳液种子聚合诱导相分离方法并结合我们发展的凝胶复合功能物质技术,首次批量制备了组成严格分区的亚微米两亲性Janus胶体颗粒(Chem. Commun.2010,46,4610;Macromolecules2010,43,5114;2011,44, 3787)。首创性得到了充分肯定(Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012,37, 445)。发展了利用界面双亲性环境,诱导溶胶-凝胶在其界面自组装制备Janus中空球方法,Janus中空球作为容器能选择性地在空腔内装载物质,为中空微球在油水分离,催化和可控装载释放等方面应用提供了新途径(Chem. Commun.2011,47,1231)。进一步选区复合高分子并控制微结构,制备了聚合物复合的多孔Janus中空球(Polymer2012,53, 3712;Macromolecules2013,46,4126)。在空腔内装载功能性纳米颗粒,如具有光催化作用的二氧化钛纳米颗粒,实现了有机染料的富积和催化降解(Chem. Commun.2013,49, 6161)。将上述Janus中空球磨碎得到Janus纳米片材料,作为颗粒乳化剂,能高效稳定流体,甚至可在空气中获得稳定的“干液滴(drydroplets)”(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2011,50, 2379)。选择生长复合物质如Fe3O4赋予其功能性如乳液液滴的磁操纵及颗粒乳化剂的磁回收。上述特性在油水分离和强化采油等领域中具有重要意义。审稿人认为“该方法简单、易于批量制备,是一类文献几乎没有报道的新材料”。相关研究结果发表后,被NatureChina和NPG Asia Materials 作为Research Highlight给予了高度评价。选区复合聚合物,实现Janus片表面不同化学分区向功能分区转化,赋予Janus片外场(磁、光、离子、温度、pH等)响应和操控性能(Macromolecules2012,45,1460;Macromolecules2013,46,2754;Chem. Commun.2014,50,5706), 为赋予Janus片外场操控和生物识别奠定了基础。研究了材料表面微结构对浸润性的影响,利用嵌段聚合物自组装特性,制备了形状规则、均一的盘状Janus材料 (Adv. Mater.2014,26, 4469;Macromolecules2013,46,7107;Macromolecules2014,47,3701)。基于以上Janus材料研究,受邀为AdvanceMaterials撰写综述(Adv.Mater.2014,26,6944)。
5、介孔复合膜
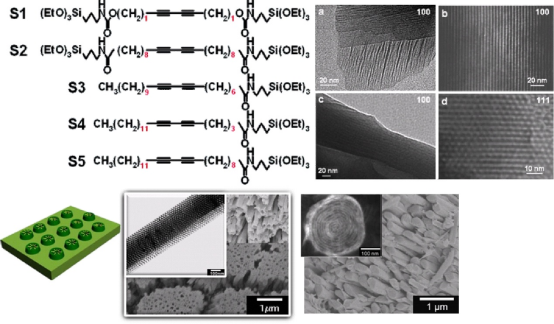
高分子链与聚集态结构的控制为制备有机-无机复合体系的物质复合与微结构控制提供了物质基础和理论依据。以嵌段共聚物超分子结构为模板,与无机物复合得到系列有序纳米孔材料,选用不同硅源物质,控制纳米孔材料骨架与孔表面的组成与化学性质。首次以多孔氧化铝膜为模板,结合二氧化硅的溶胶/凝胶和嵌段共聚物的共组装过程,制备了有机高分子/无机复合纳米有序结构膜材料和相应的一维材料和阵列体系(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2003,42,4201)。改变模板润湿性控制聚合物在受限空间的组装行为,获得了传统方法无法制备的新型特殊纳米结构。美国工程院士,纳米孔材料的开创人之一Brinker教授在其综述(Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci.2006,11,126)中对工作的首创性高度认同,认为“首次指明了氧化铝孔道受限效应影响组装结构取向排列的研究方向,一年后,Stucky等基于同样思路报道了更小空间内获得崭新的超分子结构(Nature Mater.2004,3,816);日本科学家报道了该复合膜用于纳米尺度分离纯化(Nature Mater.2004,3,337)”。首创性也得到了著名材料学家Bein教授高度认可(Adv. Mater.2011,23,2395)。相关研究工作应邀撰写综述(Chem. Commun.2009, 2270)。
6、复合多孔膜

动力电池隔膜是关键组件,约占电池总成本的30%。电池隔膜在电池过热时,通过闭孔功能阻隔电池中的电流传导,实现电池的安全保护。中国科学院化学研究所从“七五”开始就致力于高性能多孔隔膜的研制及其中的关键物理化学问题研究,提出了双向拉伸制备聚丙烯多孔(PP)隔膜的新技术,但单层结构无法满足动力电池高温闭孔保持膜完整性的需要。我们提出界面增强在PP膜基础上复合耐热涂层提高隔膜热稳定性,实现了复合隔膜的中试生产。复合膜具有多层结构,中间层高温闭孔,涂层保证隔膜完整性。与PP原膜相比,复合膜具有优异耐高温和高温闭孔特性:经180度高温处理,PP膜破裂;复合多孔膜保持完整,变得透明(表明膜已闭孔)。复合膜生产工艺能够满足电池组装线,可放量制备。充放电500次循环电池容量保持90%以上,通过过充、短路、穿刺等安全检测。对比单层PP膜,在多项测试中爆炸、冒烟。
7、纳米纤维

聚合物纳米纤维材料比表面积高、长径比高、结构组成可调,在很多方面如有机溶剂吸附、高效离子交换、水处理等方面都有潜在应用价值。自组装和静电纺丝等方法成本高,产量有限,产品耐溶剂、耐热、机械性能差,聚合物纳米纤维材料应用受到限制。我们合成了高交联的聚合物纳米纤维材料,直径在40-150 nm可控。纳米纤维可加工成多孔无纺布和块体材料,能高效吸附有机溶剂,通过挤压实现富集回收和吸附材料循环使用。对有机溶剂具有广谱性,有望在污水深度处理方面具有重大价值。 油田污水经过处理,水中原油含量小于10ppm。针对难以分离的油水乳液和农药乳液,纳米纤维可通过过滤方法实现油溶性物质吸附分离,净化水体。尤其对于水溶性有机染料污水处理尤为有效。复合改性,有望在金属离子深度处理方面实现应用。
8、药物制剂
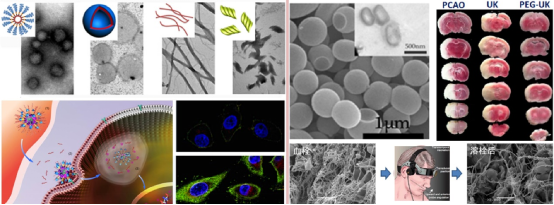
高分子药物载体的安全性和特异性是人们长期关注问题。针对肿瘤、脑卒中等治疗需求,我们设计对上述病变组织具有响应性的动态化学结构,制备了多种抗肿瘤药物和溶栓蛋白药物的高分子药物载体,实现利用化学信号和生物识别的协同作用提高载体特异性;进一步调控载体微结构、表面组成等,控制药物输送的动力学过程,满足不同的给药途径。制备了在固态肿瘤组织内具有增强内化效应的多功能聚合物载体,研究了不同剂型阿霉素/紫杉醇联合化疗对肿瘤动物模型中位生存期的影响;合成了超声响应和pH响应的尿激酶/高分子药物制剂,实现通过外场和内源性pH改变等控制蛋白药物的分布和活性,在降低蛋白药物神经毒性的同时保护血脑屏障,提高蛋白药物生物利用度并减少副作用。
Design and Synthesis of Functional Polymer Composite Materials and Understanding Their Physical and Chemical Properties
Design and synthesis of multiscale and multifunctional polymer composite is a crucial field of polymer sciences. Materials properties such as high-performance and versatility depend on that. We develop fabrication methods to control the morphology, spatial arrangement and multi-scale microstructures of the materials, in order to achieve high-performance and responsiveness of our products. Since the year of 2000, our research have focused on composite particles with complicated structures and composite membranes with nano-sized pores. We developed template-assisted fabrication and micro-processing methods to control the geometry of the materials; through the special interactions between soft matters (polymer gels and block copolymers) and other substances, we tuned their growing process as well as multi-compositional and multi-scale spatial arrangement; also, systematically, we studied the fundamental physical and chemical issues related to these materials. Recently, we have been focused on developing synthetic methods for functional Janus materials and using them for interface manipulation. Such research will provide innovative strategies to solve the problems existing in materials development, energy & environment, and biomedical applications. More details are listed as following:
1. Composite polymeric hollow spheres
Composite polymeric hollow spheres are a typical class of functional polymer composites. They serve important roles in the field of novel materials, energy, catalyst and bio-mimicking applications. Our research include systematically studying the principles of how to tune the spatial distribution of compositional moieties and the microstructures. We are the first to introduce the method of preparing hollow micro-spheres by using a functional spherical composite polymer gels template, and also elaborated the physical and chemical mechanisms of such process. We proposed a unique strategy based on the permeability and tunable functionalities of polymeric gels. The core/shell polymeric gel microspheres were used as template, then these polymeric gels can induce favorable growth of functional substances in desired sites by specific interactions.. This strategy successfully resolve the problem of continually adjusting the size and shell thickness of the hollow spheres. Our studies also revealed the physical and chemical mechanism (catalysis, electrostatic effect and ion-exchange) of such favored growth. This method had become one of the most widely used to prepare composite polymeric hollow micro-spheres. For instance, we developed a simple technique to construct nanometer channels by electric field induced structural shift and fast solidification via sol-gel process (Figure 1). Another example is by controlling the spatial distribution of functional spots of the gels, so that the functional spots of polymeric composite hollow microspheres and their microstructures (such as single/multi layers or surface bumpiness) can be arranged. Thus compartmentalizationof composition and functionalities of these hollow spheres were achieved (Figure 2). We will further improve universal preparation techniques for polymeric gel-penetrated mesostructured hollow microspheres, based on the strategy of induced favorable growth. More other hollow structures as well as inorganic species (metal, metal oxides and carbon) composited materials will be developed. We have been invited to publish a review article on Advanced Materials (2008, 20, 2965–2969.).
a)
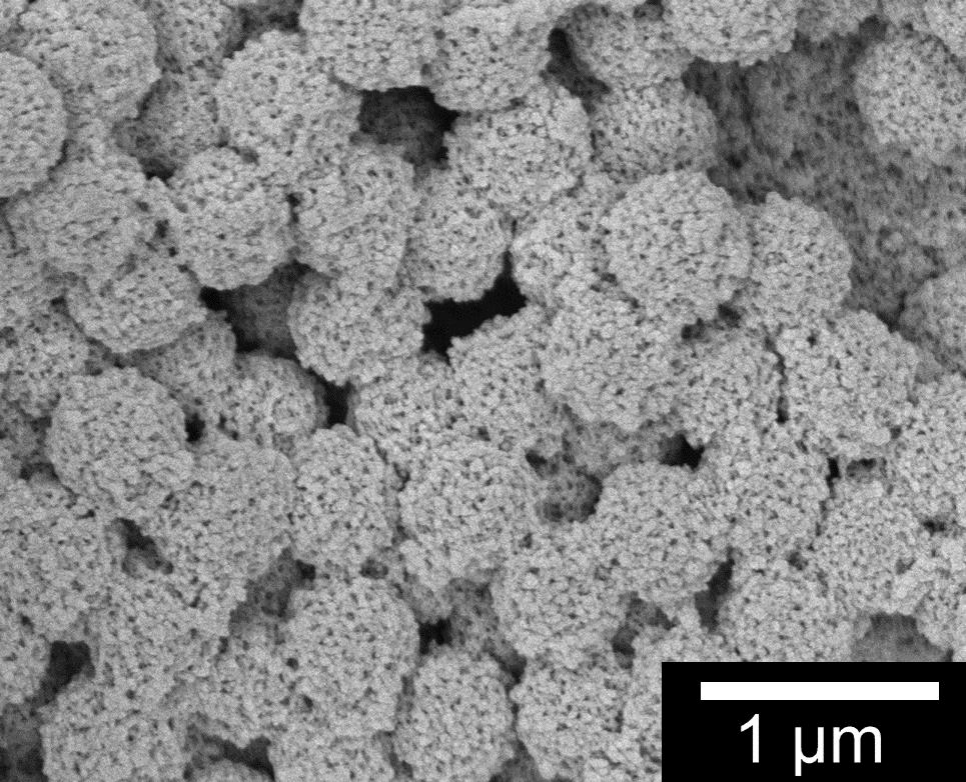 b)
b)
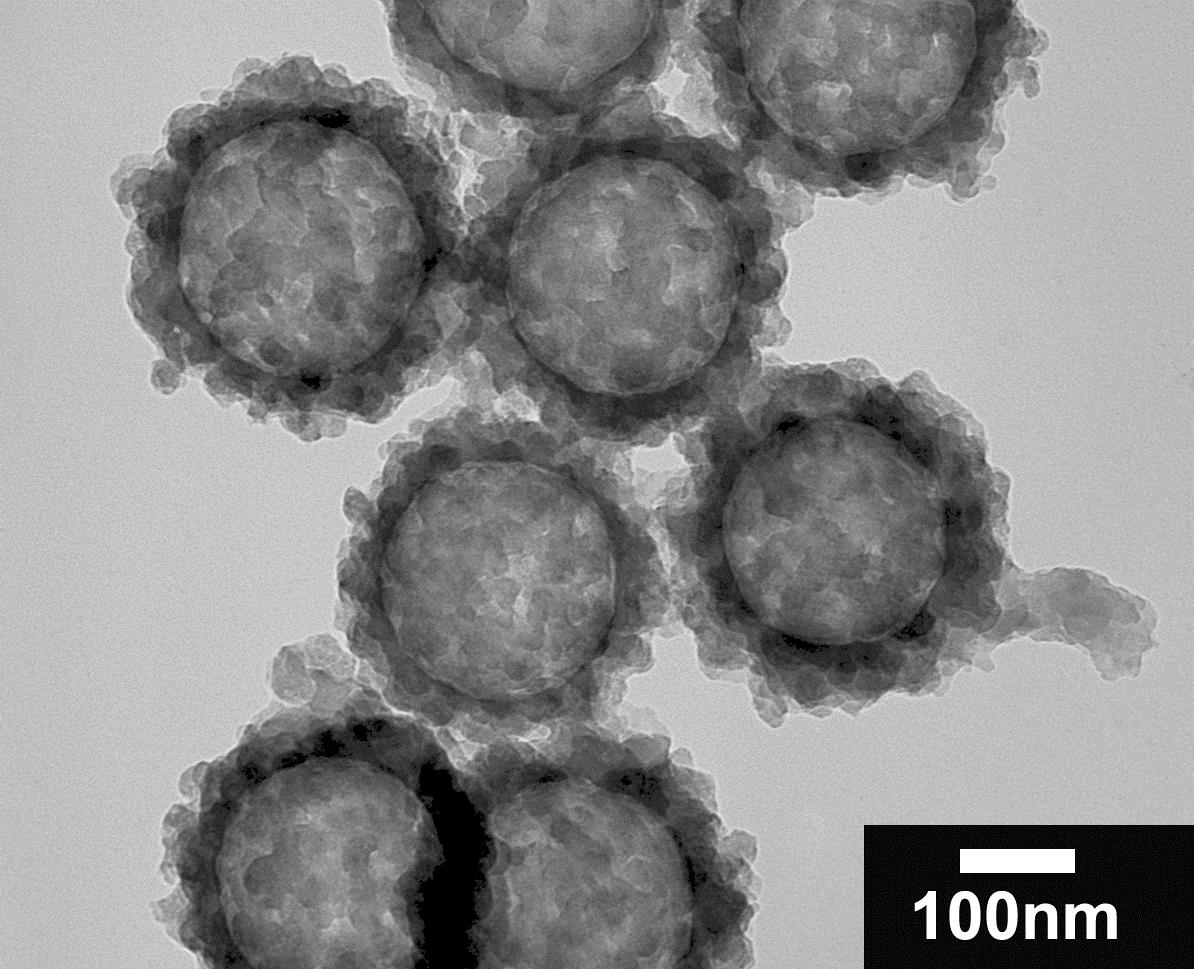

Figure 1. a) TiO2/Sulfonated polystyrene hollow porous microspheres; b) Polyaniline/SiO2 composite hollow microspheres.
a)
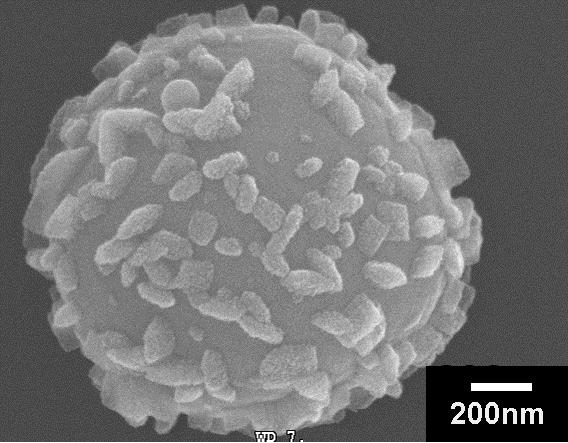 b)
b)
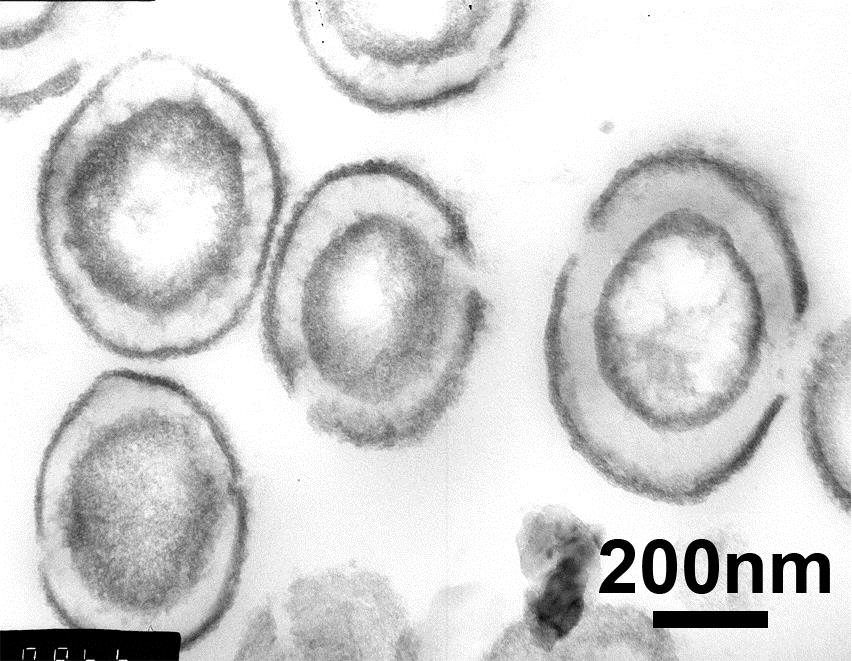
Figure 2. a) TiO2/polystyrene hollow spheres with pillars protruding out of the surface;b) Ultra-microtomed double-shelled titania hollow spheres.
2. Functional Microcapsules:
Fundamental research is the driving force for applied technologies. By applying the strategy of polymer induced favorable growth, we invented a high-efficient technique to encapsulate substance to prepare functional microcapsules, including phase-transfer heat-buffer and fire-proof capsules.The phase-transfer heat-buffer capsules are environmental friendly, and possess several advantages such as high enthalpy capacity, adjustable shell thermo-conductivity, and excellent cycling stability. They are easy to produce at low cost and we have already achieved large-scale industrialization.By cooperation with Beijing New Building Material (Group) Co., Ltd. we are able to incorporate these capsules into wall board they produce. The exhibition house built with these wall board (Figure 3a) showed outstanding energy-saving feature. The temperature data recorded inside these houses indicate that these wall board have significantly decreased daily temperature fluctuation and reduced heating/cooling energy cost in all seasons (Figure 3b).The energy saving effect isstable throughout entire experimental period for over 5 years. Our product have been put into market and practically used in several office premises in Beijing.
Other than energy conservative materials, we have also developed encapsulation technique for fire-proof reagents. The stability of the interface between the capsules and matrix was greatly improved by our methods. These fire-proof capsules are easy to use and flexible. They provide a solution for fire-proof materials under a variety of different circumstances (Figure 4).
a)
 b)
b)
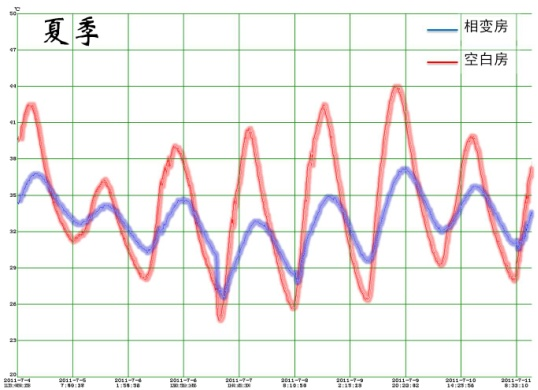
Figure 3. a) Example house built with wall board containing phase-transfer heat-buffer capsules (left), and control house built with regular wallboard (right); b) Temperature fluctuation curves(in summer) of the house built with heat-buffer capsules (blue), and control house built with regular wallboard (red).

Figure 4. Comparison of results after burning test: Regular foam plastic (left) , and foam plastic with same composition but integrated with fire-proof capsules (right)。
3. Janus composite system and interface manipulation
Janus objects have two separated compositions integrated onto the same surface, they are the typical example as compartmentalized functional materials. Our research focus on the synthetic methods of Janus particles, in order to control their composition, size and geometry. We also systematically study their physical/chemical properties and interface manipulation behaviors. Some products have already been put into large-scale production, thus their practical applications are possible (Figure 5). We have developed a facile method to synthesis sub-micron sized Janus particles with two functionalities strictly compartmentalized. Based on phase separation induced by seeded emulsion polymerization, and also utilized the aforementioned methods to prepare functional spherical composite polymer gels, we were the first to prepare the Janus particles at large scale, and built a foundation for their practical applications. We also developed a facile and highly efficient method through materialization of the interface to prepare Janus hollow spheres and nanosheets, and provided a new solution for oil-water separation, catalysis and controlled drug release (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2011,50, 2379 –2382). The reviewer evaluated such method as “Facile and suitable for large scale preparation, it is a novel class of materials which had hardly been previously reported.”Such research also received highly positive appraisals fromNature ChinaandAPG Asia Materialsas the research highlights. Furthermore, we selectively integrated functional materials onto the Janus nanosheets, and enabled them with specific capabilities such as magnetic, photonic, ionic, thermal and pH responsiveness. Laid down the ground for manipulating Janus particles with outer field and biological recognition.We were invited to publish a review article inAdvance Materials(Adv. Mater.2014,26, 6944–6949). More recently, we focus on a novel class of functional organic/inorganic composite materials, which have colloidal sizes comparable with that of the polymer molecules. We have proposed the idea of Janus Colloidal Block Copolymer, so as to integrate together the amphiphilic/self-assemble properties of block copolymers and the functionalities of nanoparticles. We believe that such research will bring new opportunities within the fields of assembly structures, interface manipulation and medical diagnosis and treatment.
Figure 5. Composite Janus materials system.
4. Organic/inorganic ordered nanostructures and mesoporous composite membrane
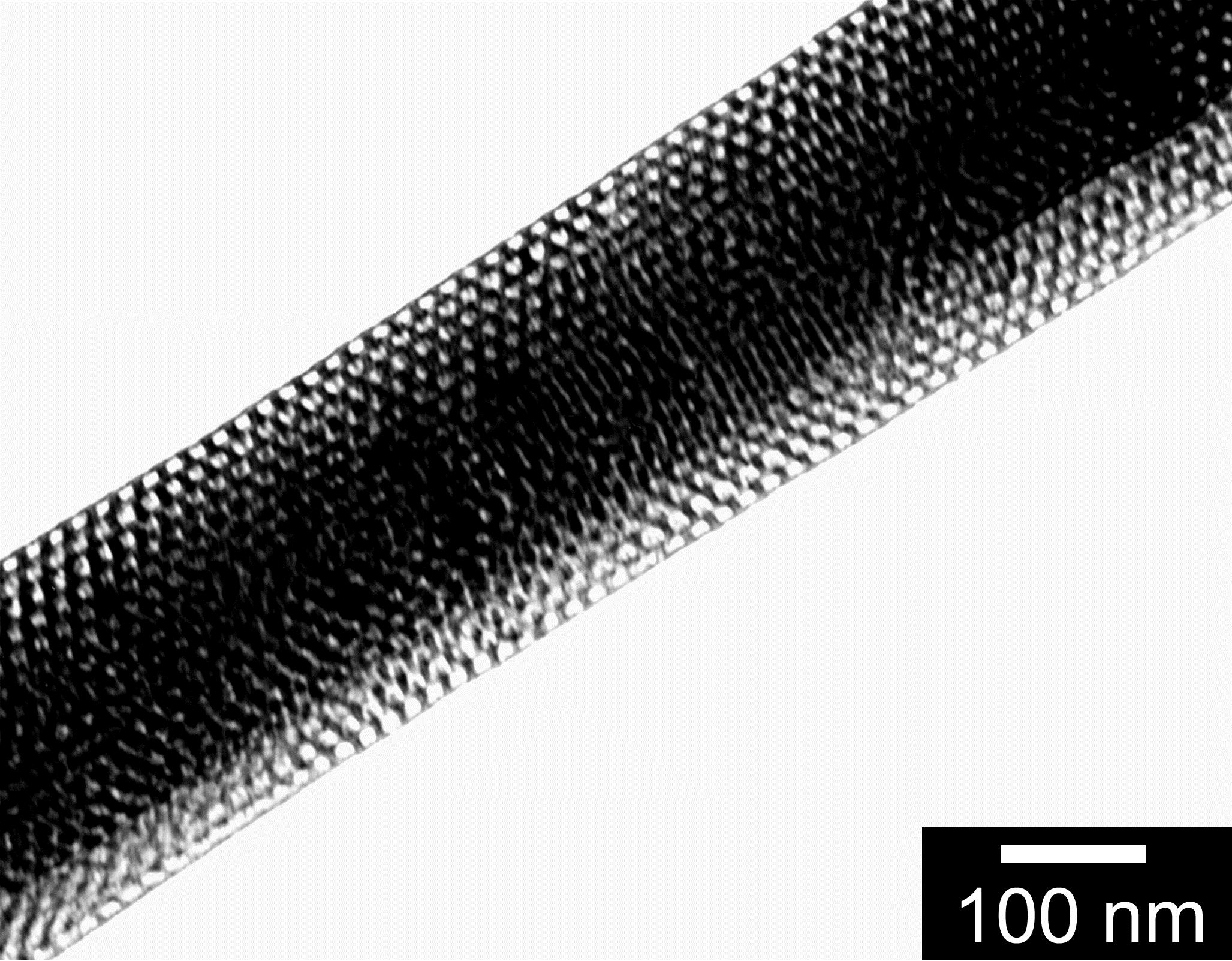
We combined the advantages of the supramolecular structures of block copolymers and the inorganic sol-gel process, and prepared a series of organic/inorganic composite and mesoporous structured materials. Through selection of different precursors, we were able to control the composition of the framework of nanoporous materials and the chemical functionalities of the pore surface. We proposed an approach to grow one-dimensional (1D) mesostructured polymer/inorganic nanocomposite membrane within the confined cylinder channels of porous anodic aluminium oxide (AAO) membranes (Figure 6). This research resolved the challenge that the diameter and aspect ratio of macroscopic pores are difficult to manipulate. By simply changing the channel pore surface wettability of the AAO membrane, the macroscopic morphology can be controlled either in the form of fibers or tubes, which the traditional methods were incapable to provide. The reviewer noted it to be “a substantial novel method to produce mesostructured materials” and a “conceptually important ideology”. Professor C. J. Brinker (Member of the NAE) have commented in his review (Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci.2006,11, 126) that this work“first noted”the“effect of confinement in nodic alumina membranes on the alignment of surfactant/silica self-assembly”. One year later, Stucky and coworkers reported smaller supramolecular structure in tighter space using similar method (Nature Mater.2004,3, 816). Shortly after that, Yamaguchi et al. proposed application of such porous membrane on nano-scale separation and purification (Nature Mater.2004,3, 337). The originality of our work was also acknowledged by Prof. Thomas Bein (Adv. Mater.2011,23, 2395). Our research is very helpful to help understand the self-assembly process in confined space at meso-scales, and provides a new approach to design micro- and nano- scale composite system. Based on the above method, we further prepared flexible and transparent polymer/inorganic mesoporous composite membrane, and built up the foundation for their large-scale applications. We have been invited to publish a review article inChem. Commun. (Chem. Commun.,2009, 2270–2277).
a)
 b)
b)

Figure 6. a) TEM image of the mesoporous silica tube; (b) mesoporous nanorods and their arrays
5. Other Research Interests
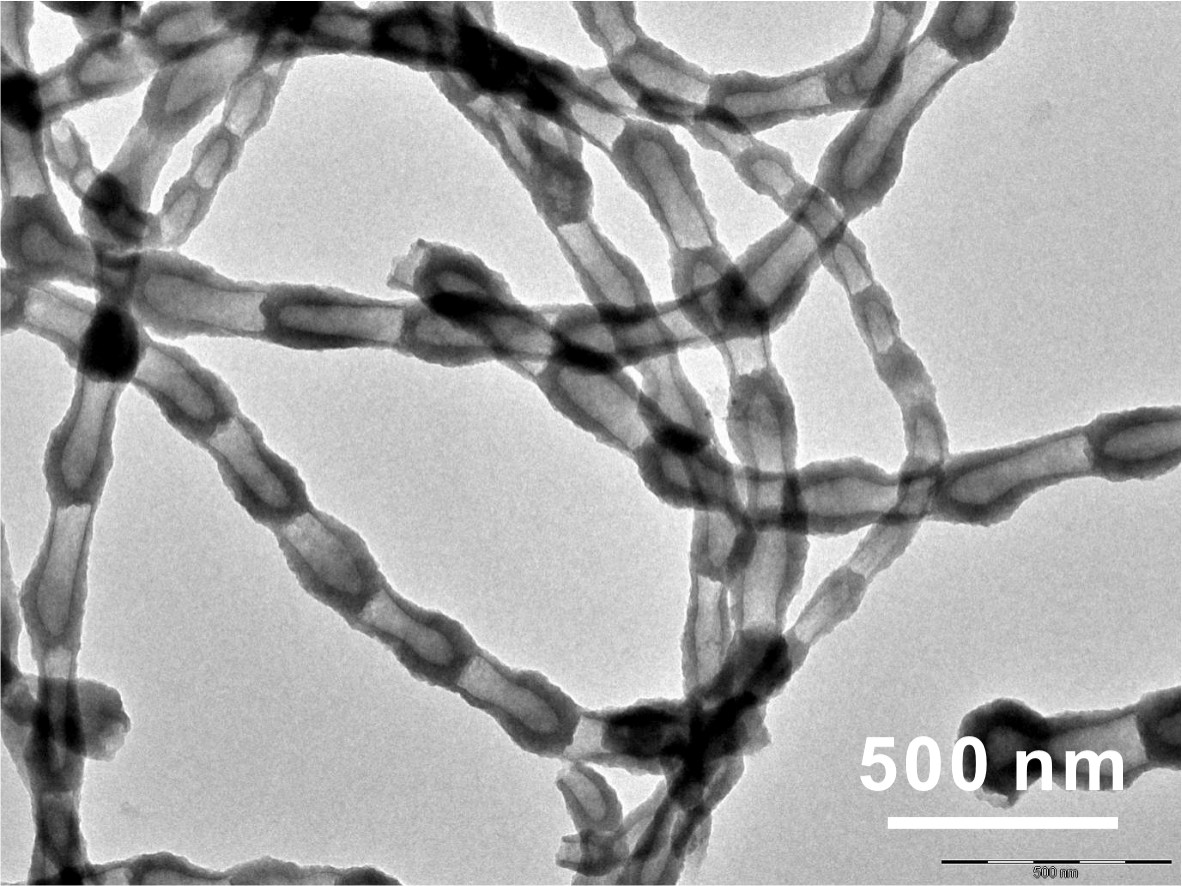
We developed the method of rapid preparation of highly-crosslinked polymeric nanofibers. The nanostructures, dimensions, composition and functionalities are tunable. These nanofibers are highly efficient and universal solvent gelation motivator. They can be used for oil-water separation purpose, and have great potential on high efficient damping system and heat-isolation.
We developed pH sensitive dynamic chemical bonding structure which are suitable within tumor cell environment. We have prepared tumor-treatment reagents such as colloidal and injectable hydrogels, to enhance the selectivity of chemotherapy drugs delivery (Figure 7b).
Aiming at the local environment within brain stem where thrombus originates, we prepared polymer/protein nanocomposite treatment system based on urokinase. Such system was applied together with super sonication to conduct thrombolytic therapy. The results showed higher uptake efficiency and could lower the occurrence of post-thrombolytichemorrhage.
a)
 b)
b)

Figure 7. a) Polymeric nanofibers;b) Extracellular responsive colloids for treatment of tumer cells.