1. Gui, Haoguan; Yang, Tiantian; Li, Li-Li; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Temperature-Sensitive Anti-Inflammatory Organohydrogels Containing Janus Particle Stabilized Phase-Change Microinclusions, ACS Nano, 2022, 16(6): 9859–9870.
A fabrication strategy for multifunctional organohydrogels is proposed, which combines phase-change microinclusions within a double-network (DN) hydrogel under the stabilization of Janus particles. Janus particles possess reactivity and colloidal stability for more robust organohydrogels, while the interstice among Janus particles enhances the mass transfer between the phase interfaces. Moreover, DN hydrogels are achieved through dynamic cross-linking networks, endowing organohydrogels with injectability and self-healing performance. Phase-change microinclusions are beneficial to the organohydrogels with temperature-responsive mechanical property and temperature-programed shape-memory performance. Organohydrogels can be employed for temperature therapy through the melting-crystallization process of phase-change microinclusions. Simultaneously, the payloads within microinclusions can be released for antibacteria upon melting the encapsulated wax. The organohydrogels can be served as an ideal dressing with temperature-responsive mechanical property, temperature therapy effectiveness, and temperature-triggered antibacterial ability.
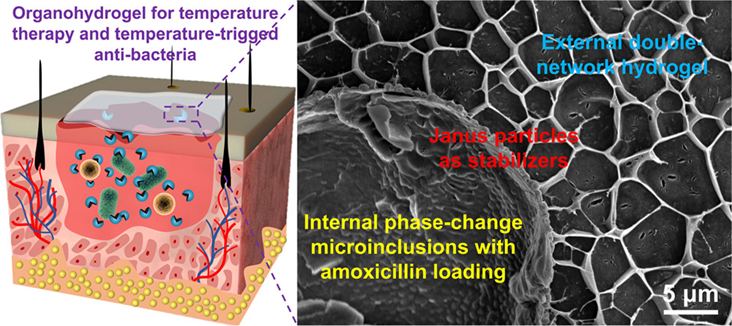
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c03940
2. Shao, Yue; Ye, Yilan; Sun, Dayin; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Polymer-Derived Janus Particles at Multiple Length Scales, Macromolecules, 2022, 55(15): 6297–6310.
Polymer-derived Janus particles, both polymeric and composites of organic and inorganic components, hold promise as key elements in future applications due to their unique morphologies and functionalities. In this Perspective, recent progress in the synthesis and generation of polymer-derived Janus particles at the single-chain, nanoscopic, and macroscopic length scales is described. We focus on significant achievements in the control of distinct compartmentalization and large-scale synthesis of Janus nanoparticles, both of which are crucial for their practical use. The challenges and opportunities associated with polymer-derived Janus particles are outlined to inspire the development of new strategies for the large-scale synthesis of Janus particles with integrated functionalities.

https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.2c00512
3. Shao, Yue; Wang, Yong-Lei; Tang, Zian; Wen, Zhendong; Chang, Chiawei; Wang Chunyu; Sun, Dayin; Ye, Yilan; Qiu, Dong; Ke, Yubin; Liu, Feng; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Scalable Synthesis of Photoluminescent Single-Chain Nanoparticles by Electrostatic-Mediated Intramolecular Crosslinking, Angewandte Chemie, 2022, 134(27): e202205183.
We report the large-scale synthesis of photoluminescent single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) by electrostatic-mediated intramolecular crosslinking in a concentrated solution of 40 mg mL-1 by continuous addition of the free radical initiator. Poly(vinyl benzyl chloride) was charged by quaternization with vinyl-imidazolium for the intramolecular crosslinking by using 2,2-dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone (DMAP) as the radical initiator. Under the electrostatic repulsion thus interchain isolation, the intrachain crosslinking experiences the transition from coil through pearl-necklace to globular state. The SCNPs demonstrate strong photoluminescence in the visible range when the non-emissive units are confined thereby. Composition and microstructure of the SCNPs are tunable. The photoluminescent tadpole-like Janus SCNP can be used to selectively illuminate interfacial membranes while stabilizing the emulsions.
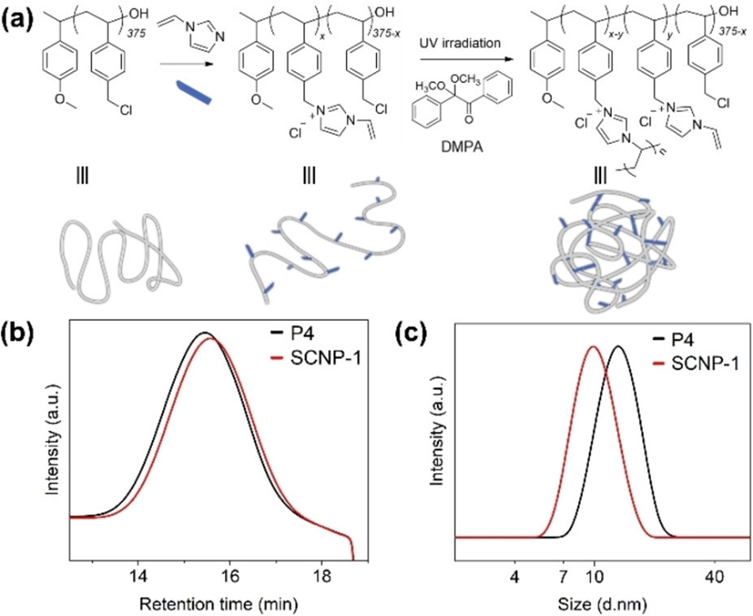
https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202205183
4. Zhang, Meng; Jiang, Chao; Wu, Qiuhua; Zhang, Guolin; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene succinate) (PLA/PBS) Layered Composite Gas Barrier Membranes by Anisotropic Janus Nanosheets Compartibilizers, ACS Macro Letters, 2022, 11(5): 657–662.
Poly(lactic acid) (PLA), one of the most promising biodegradable polymer products, has achieved wide applications for its relatively good mechanical properties and moderate degradability. Here we report an environment-friendly filler, the organic–inorganic composite Janus nanosheets (PLA/PBS JNs), which can jam at the interface of the PLA/PBS blend with a low threshold as the compatibilizer and can simultaneously toughen the composites and improve the gas barrier performance due to better interfacial interaction and tortuous path effect. With 0.3 wt % of PLA/PBS JNs added, the tensile strength and elongation at break of the PLA/PBS blend can be improved by 37% and 224%, respectively. After a further hot-pressing process, the barrier performance of the PLA/PBS composite membranes can be significantly enhanced since PLA, PLA/PBS JNs, and PBS are arranged in a nearly lamellar structure with oxygen permeability of 0.63 × 10–15 cm3 cm·cm–2 s–1 Pa–1 with only 0.5 wt % of PLA/PBS JNs.

https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.2c00139
5. Wang, Chunyu; Liu, Yingze; Shao, Yue; Tang, Zian; Wen, Zhendong; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Zwitterionic Polymer Hairy Coating onto Mesh toward Easy Oil/Water Separation, Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2022, 43(8): 2200016.
A zwitterionic polymeric hair-coated stainless steel mesh membrane is fabricated, which demonstrates efficient separation of oil/water mixtures and emulsions. The hairy coating of poly(divinylbenzene-co-vinylbenzene chloride) is generated by precipitation cationic polymerization, and subsequently grafting a zwitterionic polymer layer by atom transfer radical polymerization of sulfobetaine methacrylate. The microstructure of the hairy coating is tunable from an array of individual nanofibers to porous networks by interweaving of the hairs. The long-range attraction of zwitterionic polymers with water renders the coated mesh with excellent superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic performance. The coated mesh is highly antifouling to avoid the prehydration in conventional methods. Moreover, the microstructure is demonstrated to be responsible for the high separation efficiency of oil/water emulsion. Therefore, separation of oil/water mixtures and emulsions becomes easier by the coated mesh, which is promising in industrial oil field sewage treatment.

https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202200016
6. Shao, Yue; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Progress in polymer single-chain based hybrid nanoparticles, Progress in Polymer Science, 2022, 133: 101593.
Precise control of molecular hierarchical organization has endowed biological systems with unique functions, which inspires great efforts in the synthesis of artificial mimics. Polymeric single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) with tunable microstructure and composition and distinct compartmentalization features are regarded as an ideal platform for biomimetic architectures. SCNPs represent an intermediate state between polymer and colloidal matter and are constructed by intramolecular crosslinking of linear polymers with tailored composition and topology. The microstructure of the SCNPs is broadly tunable from individual particle, to tadpole-shaped and dimer by using the polymers with different sequential distribution. It is noted that cyclic polymers are regarded as specific SCNPs with well-defined number of knotting (crosslinking). Functional composite hybrids are derived whose head and chain parts are greatly enriched in composition and microstructure via selective growth of functional materials or post-modification. Synergistic effects can emerge through hybridization of functionalities of the colloidal nanoparticles and characteristics of the polymer chains. These hybrids are attractive for applications such as the fabrication of novel superstructures that mimic catalytic functionalities of enzymes. This review summarizes recent advances in the synthesis of SCNP based functional hybrid nanoparticles. Large-scale synthetic approaches of the hybrid nanoparticles are highlighted. The use of SCNP as platform for functional hybrid nanoparticles is subsequently illustrated by applications such as biomimetic catalysis, interfacial engineering and biomedicine.

https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2022.101593
7. Hou, Hanyi; Yang, Tiantian; Zhao, Yanran; Qi, Meiyuan; Song, Zhining; Xiao, Yi; Xu, Lai; Qu, Xiaozhong; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Janus Nanoparticle Coupled Double-Network Hydrogel, Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2022: e2200157.
For double network (DN) hydrogels, their performance can be tuned by adjusting the interaction between their two networks. A novel DN hydrogel toughening approach is proposed by employing Janus nanoparticles (JNs) as crosslinkers to gain a conjoined-network hydrogel. First, a kind of JNs modified by amino groups and quaternary ammonium salt is synthesized, named R3N+-JN-NH2. The DN hydrogel is fabricated based on ionic coordination between calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium alginate (Alg), as well as covalent (benzoic imine) between glycol chitosan (GC) and benzaldehyde-capped poly(ethylene oxide) (BzCHO–PEO–BzCHO). Based on the same covalent and ionic dynamic crosslinking mechanism, the added R3N+-JN-NH2 interacts with two networks to promote crosslinking to form a dually crosslinked structure. The R3N+-JN-NH2 effectively provides more energy dissipation, and the hydrogel with conjoined networks shows better compression resistance.

https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202200157
8. Chen, Zhuo; Yuan, Jifang; Dong, Yuhang; Liu, Haipeng; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Wang, Yundong; Xu, Jianhong; Efficient recovery and enrichment of rare earth elements by a continuous flow micro-extraction system, Fundamental Research, 2022, 2(4): 588–594.
The excessive exploitation of rare earth elements (REEs) has caused major losses of non-renewable resources and damage to the ecosystem. The processes of mining and smelting produce massive amounts of wastewater with low concentrations of REEs. Consequently, the enrichment and recovery of low-concentration REEs from wastewater has significant economic and environmental value. For this purpose, operation under large phase ratios (the flow rate ratio between the aqueous phase and extractant) is more desirable and economically viable. However, the traditional REE extraction process suffers from the uneven dispersion of the extractant and the difficulty of phase separation, which leads to long extraction times and large consumption of extractants. Hence, there is an urgent need to develop a green and efficient technique to extract low concentrations of REEs from wastewater. In this work, a droplet-based microfluidic technique was used to continuously extract and recover low-concentration REEs at large phase ratios. Snowman-shaped magnetic Janus nanoparticles were added to the continuous phase as emulsifiers to facilitate uniform extractant dispersion and rapid phase separation. Several key factors affecting the extraction efficiency, including pH, residence time, and the amount of added Janus nanoparticles, were systematically investigated. Compared to batch extraction, droplet-based microfluidic extraction with the addition of Janus nanoparticles showed the advantages of a large specific surface area and fast phase separation during extraction. Meanwhile, the Janus nanoparticles exhibited good emulsification performance after three extraction cycles. In summary, the Janus nanoparticle-stabilized droplet generated by microfluidic methods provides a feasible path for the efficient enrichment and recovery of low-concentration REEs.
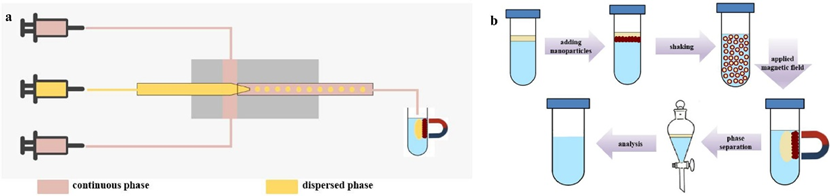
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fmre.2021.06.019
9. Liu, Yijiang; Wang, Jialin; Shao, Yue; Deng, Renhua; Zhu, Jintao; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Recent advances in scalable synthesis and performance of Janus polymer/inorganic nanocomposites, Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 124: 100888.
Janus nanomaterials composed of two compartments with dissimilar compositions and/or functionalities have garnered considerable interest over the past several decades owing to their diverse nanostructures and intriguing properties arising from the two constituents and microstructures. Janus polymer/inorganic nanocomposites represent a class of unique materials that afford synergistic features of polymers and inorganic substance, rendering appealing properties and promising applications. Various synthetic routes have been developed to craft a host of Janus materials with tunable composition, morphology and microstructures. This review focuses on the recent advances in rational design, precision synthesis, and performance of a set of Janus polymer/inorganic nanocomposites. Four main synthetic strategies are discussed, including Pickering emulsion interfacial synthesis, conventional emulsion interfacial synthesis, confined self-assembly of block copolymers, and seeded swelling emulsion polymerization. The detailed synthetic methods and strictly Janus characteristics are highlighted. This review aims to attract broad interests in the polymer and nanomaterial communities by directing the research focus on judicious design and synthesis as well as large-scale production of Janus polymer/inorganic nanocomposites, thereby imparting the further exploration of their extraordinary attributes and practical applications.
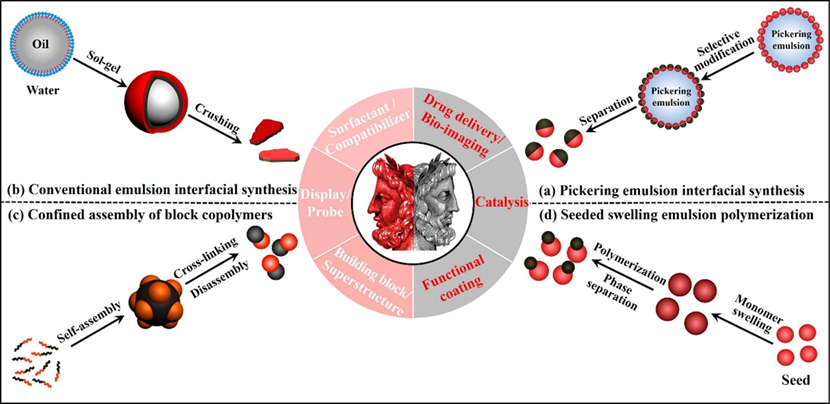
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2021.100888