Research Articles
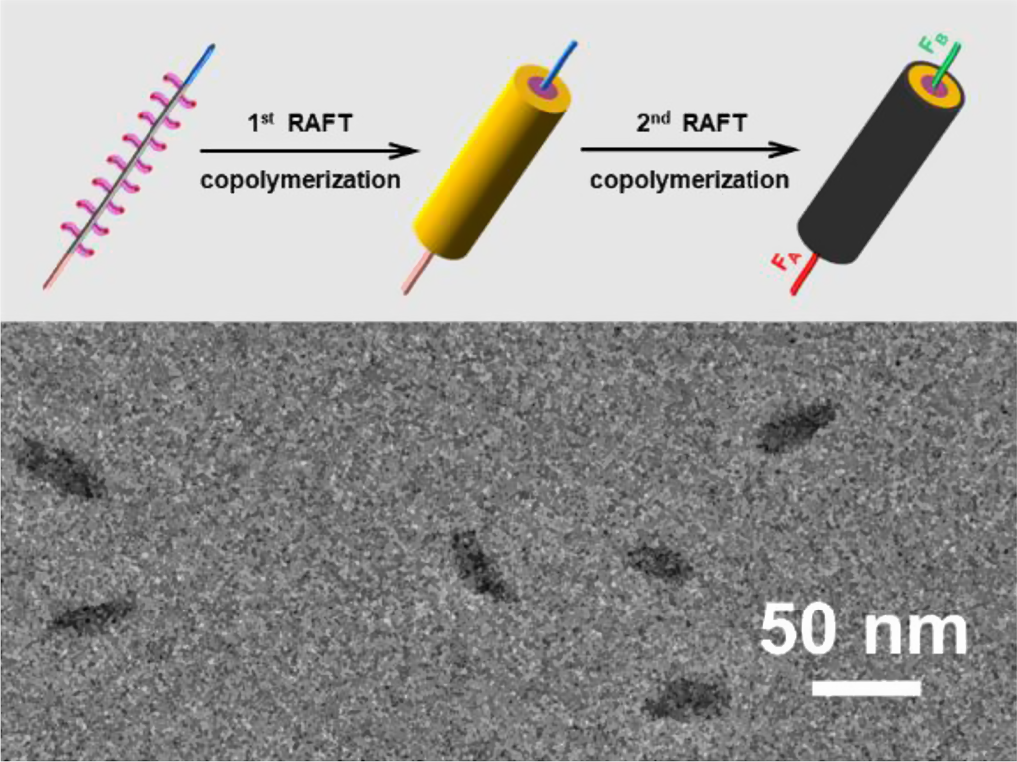
1. Wen, Zhendong; Li, Fenglin; Qu, Kairu; Sun, Dayin; Yang, Hua; Zhu, Jintao; Nie, Zhihong*; Lin, Zhiqun*; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Large-Scale Synthesis of Janus Polymer Nanorods via Electrostatics-Mediated Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization in Concentrated Solutions. CCS Chem., 2026, 8, 246-260.
Janus polymer nanorods with tunable compositions and microstructures possess directionally specific interactions, enabling their self-assembly into hierarchically structured materials (e.g., biomimetic pillared nanostructures). Traditional synthesis methods usually require highly dilute conditions (<1 mg/mL) to prevent aggregation. Herein, we report the synthesis of Janus polymer nanorods by electrostatics-mediated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer copolymerization of cross-linkers and monomers from polymer bottlebrushes. This method achieves an unprecedentedly high solid content over 100 mg/mL, that is, two orders of magnitude higher than that attainable by conventional approaches. The composition, microstructure (e.g., multilayered architecture), and characteristic dimension of the nanorods are broadly tunable. As a representative example, AB-type Janus nanorods are derived by orthogonal modifications of the end blocks, introducing desired functional groups to drive directional interactions. The Janus nanorods serve as building blocks to self-assemble into diverse superstructures from nanowires to continuous networks, providing a facile platform for the in-situ construction of functional materials within suitable matrices.
https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.025.202506889
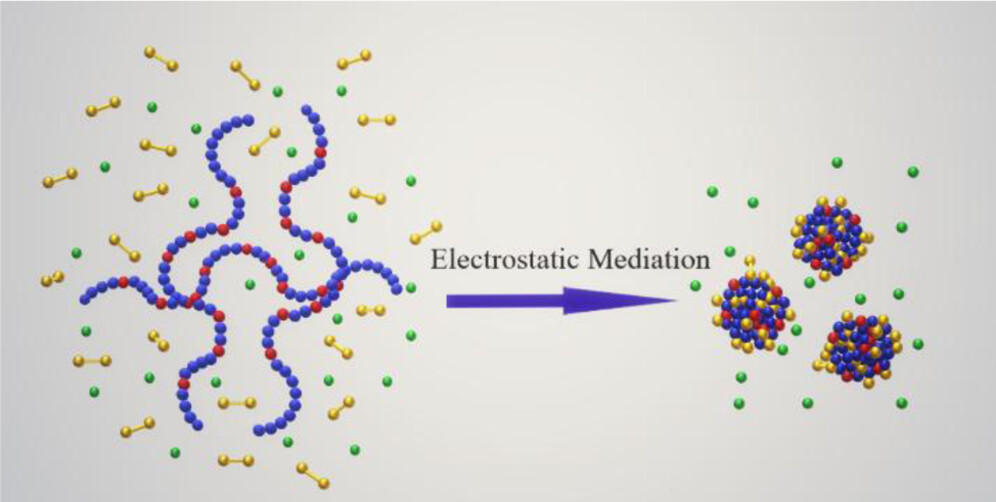
2. Wang, Dan; Zhong, Zhixuan; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Jiang, Jian*. Electrostatic Mediation in Synthesis of Single-Chain Nanoparticles in Concentrated Solutions. Macromolecules, 2026, http://doi/10.1021/acs.macromol.5c02798
Rational design and large-scale synthesis of polymer single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) via intramolecular cross-linking of polymers in concentrated solutions is of great significance in polymer and nanomaterials science. It is urgently required to develop methods to suppress intermolecular cross-linking in highly concentrated polymer solutions. Yang et al. have recently proposed a novel effective method of electrostatics-mediated intramolecular cross-linking of polymer single-chains in concentrated solutions. Herein, we develop a scaling theory and perform large-scale dissipative particle dynamics simulation to elucidate the key role of electrostatic mediation in the intramolecular cross-linking. Specifically, the effectiveness of electrostatic repulsion, hence electrostatic mediation, is confirmed, which exhibits a nonmonotonic dependence on electrostatic strength. The effectiveness is enhanced to the maximum when the electrostatic strength is increased to the transition boundary between the weak and strong electrostatic coupling regimes. Such nonmonotonic behavior is attributed to the onset of counterion condensation to suppress the formation of SCNPs under strong electrostatic coupling conditions. The current finding helps to further understand the electrostatic mediation and guides the design and large-scale synthesis of SCNPs in concentrated solutions.