1. Lang, Fengzheng; Xiang, Dao; Wang, Jiawei; Yang, Liping; Qiao, Yan; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Janus Colloidal Dimer by Intramolecular Cross-linking in Concentrated Solutions, Macromolecules, 2020, 53(6):2271-2278.
We propose a new method to large-scalesynthesize polymeric colloidal dimers by electrostatically-mediatedintramolecular cross-linking of an example di-block copolymer of poly(isoprene)-b-poly(vinylpyridine) (PI-b-P4VP) in highly concentrated solutions.The synthesis is orthogonally performed in a highly polar solvent such as DMSO.The first colloid is achieved by intramolecular cross-linking of the PI block with 1,6-hexanediisothiocyanate after modification with 2-mercaptoethylaminehydrochloride to introduce an electrostatic interaction. The Janus single-chainnanoparticle of cPI-P4VP is derived. In the sequential step, the other colloidis achieved by intramolecular cross-linking the P4VP block of cPI-P4VP with 1,5-diiodopentaneafter modification with iodoethane. The polymer colloidal dimer of cPI-cP4VP isthus achieved. The Janus cPI-cP4VP dimer is composed of two different domains:the cPI containing residual amine and cyanate groups and the cP4VP containing residual pyridine and quaternized groups. The dimer can be synthesized at a higher concentration of 100 mg/mL. A huge family of functional colloidal dimers is expected after selectively loading materials within the desired colloidal domains.
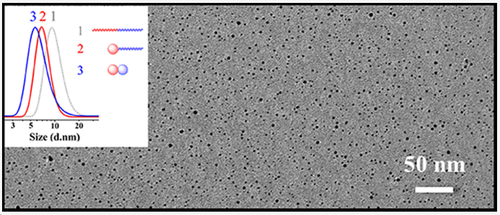
DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00180
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00180
2. Yang, Liping; Xu, Jingjing; Wang, Jiawei; Lang, Fengzheng; Liu, Bing; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Responsive Single-Chain / Colloid Composite Janus Nanoparticle, Macromolecules, 2020, 53(6): 2264-2270.
A facile approach is reported toward a thermoresponsive single-chain/colloid composite Janus nanoparticle by the termination of the corresponding anionic living single polymer chain onto the chlorine-capped Fe3O4 nanoparticle. Poly(2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethyl methacrylate)(PMEO2MA) is selected as an example of a thermoresponsive polymer, which can be easily synthesized by anionic living polymerization. The Janus nanoparticle serves as a highly effective thermoresponsive solid surfactant, which can be manipulated with a magnet. The Janus/hydrophobicreversible transition can be triggered by near-infrared (NIR) irradiation to occur at a lower surrounding temperature owing to the photothermal effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticle. Integration of thermal response from PMEO2MA and paramagnetic and photothermal effects from Fe3O4 within the Janus nanoparticle, a powerful tool is provided to easily control the stability and microstructure of the emulsions.
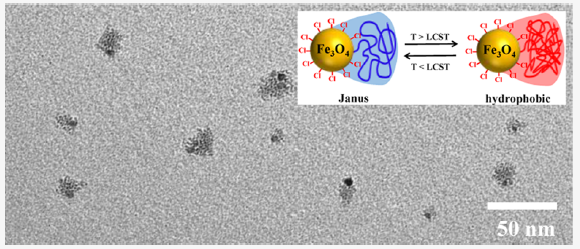
DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00109
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00109
3. Wang, Jiawei; Chen, Xi; Lang, Fengzheng; Yang, Liping; Qiu, Dong; Yang,Zhenzhong*. Large Scale Synthesis of Single-chain/Colloid Janus Nanoparticles with Tunable Composition, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56: 3875-3878.
A general approach is proposed to large scale synthesize tadpolelike composite Janus nanoparticles(JNP). Within the head of a starting JNP achieved by electrostatic-mediated intramolecular crosslinking, a free radical initiator is incorporated. By polymerizing vinyl monomers within the head nanoreactor, composition and performance of the JNPs are broadly tunable.

DOI: 10.1039/D0CC00686F
https://dx.doi.org/10.1039/D0CC00686F
4. Xiang, Dao; Jiang, Bingyin*; Liang, Fuxin; Yan, Litang; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Single-Chain Janus Nanoparticle by Metallic Complexation, Macromolecules, 2020, 53(3): 1063-1069.
Single-chain Janus nanoparticle of the example polymer polystyrene-blockpoly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-polyethylene oxide(PS-b-P2VP-b-PEO) was achieved by intramolecular cross-linking via complexation of P2VP with cobalt octacarbonyl, while themetallic complex was incorporated within the cross-linked core. It is crucial to introduce electrostatic interaction along the chain by pretreatment and thus ensure the intramolecular cross-linking in concentrated solutions, for example, 30 mg/mL. After thermolysis in the dispersion, the complex is decomposed achieving cobalt within the P2VP core. A magnetic responsive single-chain Janus composite nanoparticle was derived with the P2VP/Co core conjugated with PS and PEO single chains onto the opposite sides. The Janus composite nanoparticle displays highly catalytic activity and magnetic responsive performance from themetallic cobalt and interfacial activity from the PS and PEO single chains. A highly efficient catalytic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds at emulsion interfaces was demonstrated thereby, which was easily recycled with a magnet.

DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02388
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02388
5. Shi, Siyu; Zhang, Linlin; Zhang, Guolin; Song, Ximing; Sun, Dayin*; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Jellyfish-Like Janus Polymeric Cage, Macromolecules, 2020, 53(6): 2228-2234.
We report a new jellyfish-like Janus polymeric cage and its synthesis by two-step emulsion interfacial polymerization. The “head” part is generated by the free-radical polymerization of styrene/divinylbenzene in the paraffin emulsion droplet. A hydrophilic polymer layer, for example, polyacrylamide is coated onto the exposed side of the head by further feeding the monomer during the polymerization.The “belly” part is achieved in the second emulsion interfacial polymerization by copolymerizing the hydrophobic monomers in the internal paraffin phase with hydrophilic monomers such as acrylic acid in the external aqueous phase. The “head” and “belly” parts are covalently connected, making the Janus cage robust in solvents. The “belly” shell is composed of a hydrophobic interior surface and a hydrophilic exterior surface, which are responsible for selective loading of organic species from the aqueous surroundings. The Janus contour surface of the cage is responsible for delivering the cargo toward the targets.
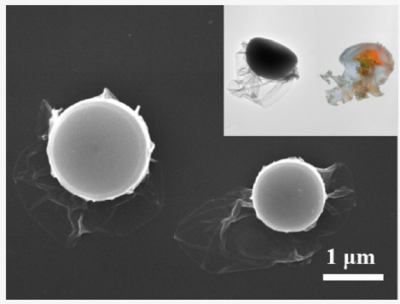
DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00166
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00166
6. Sun, Zhu; Yang, Chenjing; Wang, Fan; Wu, Baiheng; Shao, Baiqi; Li,Zhuocheng; Chen, Dong*; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Liu, Kai*. Biocompatible and pH-Responsive Colloidal Surfactants with Tunable Shape for Controlled Interfacial Curvature, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(24): 9365-9369.
Molecular surfactant-stabilized emulsions are susceptible to coalescence and Ostwald ripening. Amphiphilic particles,which have a much stronger anchoring strength at the interface, could effectively alleviate the problems, forming stable Pickering emulsions. Here, we develop aversatile method to fabricate biocompatible amphiphilic dimer particles via controlled co-precipitation and phase separation. The dimer particles consistof a hydrophobic PLA bulb and a hydrophilic shellac-PEG bulb, resembling nonionic molecular surfactants. The size and diameter ratio of the dimer particles are easily tunable, giving a flexible control over the water/oil interfacial curvature and thus the type of emulsions. The particle-stabilized emulsions are stablefor a long period of time and could be destabilized through a pH-triggered response. The biocompatible amphiphilic dimer particles with tunable morphology and functionality are thus ideal colloidal surfactants for various applications.
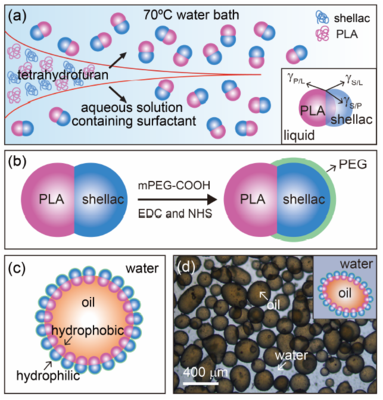
DOI:10.1002/anie.202001588
https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.202001588
7. Li, Dan#; Chen, Xi#; Zeng, Min; Ji, Jinzhao; Wang, Yun; Yang,Zhenzhong*; Yuan, Jinying*. Synthesis of ABn-Type Colloidal Molecules by Polymerization-Induced Particle-Assembly (PIPA), Chem. Sci., 2020, 11: 2855-2860.
Conventional synthesis of colloidal molecules (CMs) mainly depends on particle-based self-assembly of patchybuilding blocks. However, direct access to CMs by the self-assembly ofisotropic colloidal subunits remains challenging. Here, we report the mass production of ABn-type CMs by polymerization induced particle-assembly(PIPA), using a linear ABC triblock terpolymer system. Starting from diblock copolymer spheres, the association of spheres takes place in situ during the polymerization of the third block.The third blocks aggregate into attractive domains, which connect spheres into CMs. The stability of CMs is ensured, as long as the conversions are limited to ca. 50%, and the pH is low. The valence of ABn-type CMs (n=2–6) is determined by the volume ratio of the polymer blocks. By tuning the volume ratio, 78.5% linear AB2-type CMs are yielded. We demonstrate that polymerization-induced particle assembly is successful for the scalable fabrication of ABn-type CMs (50 g L_1), and can be easily extended to vastly different triblock terpolymers, for a wide range of applications.

DOI:10.1039/d0sc00219d
https://dx.doi.org/10.1039/d0sc00219d
8. Guan, Song; Wen, Wei; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Chen, Aihua*. Liquid Crystalline Nanowires by Polymerization Induced Hierarchical Self-Assembly, Macromolecules, 2020, 53(1): 465-472.
By taking advantage of strong liquid crystallization ordering and photo dimerization of the mesogen stilbene,we propose large-scale synthesis of nanowires of stilbene-containing block copolymers by polymerization induced hierarchical self-assembly. The interior of nanowires is in the type of liquid crystal (LC) structure with highly orderedsmectic LC layers, which are perpendicular to the long axis. The alternative striped structure consists of the polymethacrylate backbone and stilbene-containing side chain. The approach is general towards tilbene-containing block copolymer LC nanowires, irrelevant with the composition of stabilizer blocks. The nanowires become robust with the layered structure preserved after cross-linking via dimerization upon UV irradiation. The nanowires reported here may provide one dimensional model blocks toward superstructures,which can be used in the fields of electric nanoconductors, functional additives, etc.

DOI:10.1021/acs.macromol.9b01757
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.9b01757
9. Meng, Hongyu; Wan, Jiping; Jing, Jingyun; Sun, Dayin; Jiang, Bingyin; Liang, Fuxin; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Magnetic responsive Polymer Nanofiber Composites for Easy Collecting Chemical Spills, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2020, 31(1): 253-255.
We describe asimple method to prepare magnetic responsive polydivinylbenzene (PDVB) nanofiber composites by precipitated cationic livingpolymerization in the present of oleic acid capped Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs). The Fe3O4 NPs are encapsulated with the PDVB forming dendrites, from which thin nanofibers are grown in the tip-growth mode. The thin nanofibers are interwoven with the thick nanofibers forming robust composite network. The composites are magnetic responsive and highly efficient to gel almost all chemicals. Separation of the gelled chemicals from water becomes easier with a magnet. The performance is promising for magnetic collection of chemical spills.

DOI: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.04.002
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.04.002