Research Articles
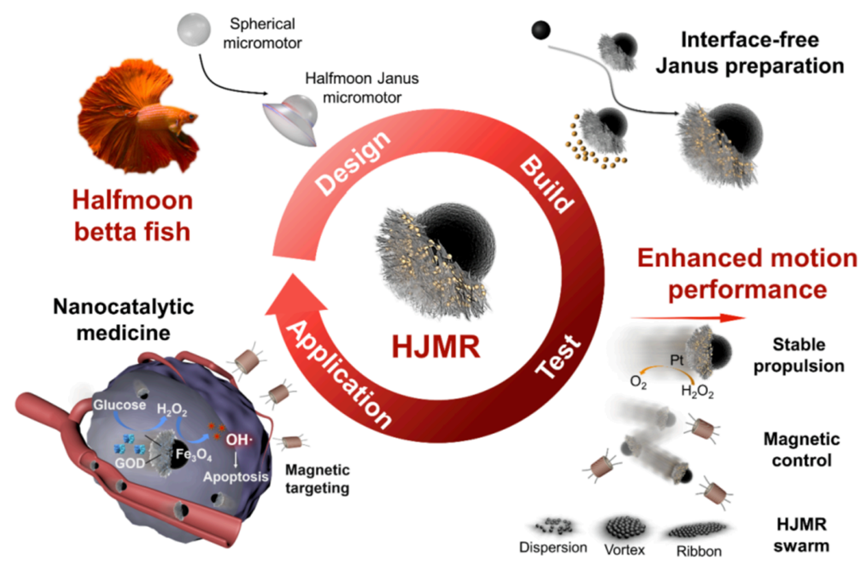
1.Liu, Dong; Sun, Dayin; Zhou, Jiaxin; Liu, Haoran; Guo, Ruirui; Wang, Bin; Ma, Wenjun; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Lu, Yuan*. Bionic morphological design and interface-free fabrication of halfmoon microrobots with enhanced motion performance, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 452: 139464.
Micro/nanorobots with the ability to explore the microworld have attracted extensive research interest for the promising biomedical application. However, the extremely low motion stability and efficiency by active self-propulsion and remote control at the sub-micron scale greatly limit its practical application. The morphological structure of micro/nanorobots with high kinetic stability and efficiency needs to be designed and prepared. Here, inspired by halfmoon betta fish, the halfmoon Janus microrobots (HJMRs) with stable directional motion performance at the sub-micron scale were developed. Through modeling analysis, the halfmoon morphology was proved a better anti-interference ability to the fluid and irregular Brownian motion than other morphologies. An interface-free Janus preparation method was developed for the production of halfmoon Janus nanoparticles and asymmetric loading of platinum to prepare HJMRs. Benefiting from the bionic rational morphological design, HJMR showed enhanced directional motion performance under chemical propulsion. HJMR also presented programmable motion control and transformable swarm control using magnetic field. HJMR was further utilized as active catalytic carriers to execute tumor-targeted propulsion and trigger the tumor-selective cascade reaction for active tumor therapeutics. The rational morphological design of microrobots with enhanced motion performance and the universal interface-free Janus preparation holds considerable promise for the large-scale production of active Janus microrobots and practical biomedical applications.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139464
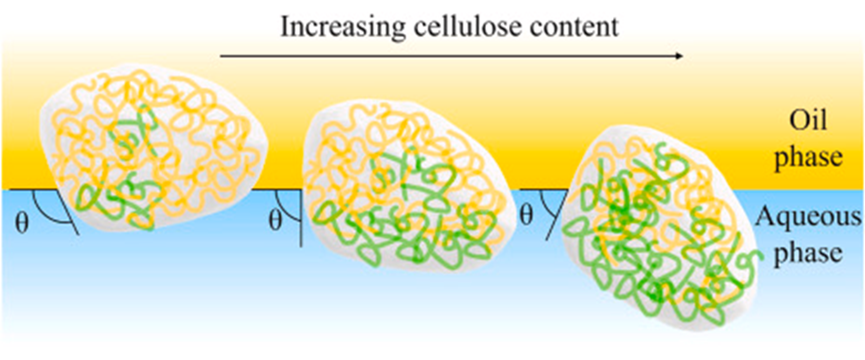
2.Wang, Yijie#; Li, Xiufeng#; Li, Ting; Wang, Yang; Jiang, Jie; Zhang, Xuhui; Huang, Jing; Xia, Bihua; CheungShum, Ho; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Dong, Weifu*. Ultra-stable pickering emulsions stabilized by zein-cellulose conjugate particles with tunable interfacial affinity, Food Hydrocolloids, 2023, 134: 108055.
Designing solid particles with desirable interfacial affinity from plant-based ingredients is a key area in sustainable food production. Here, a chemical approach is introduced to fabricate conjugate particles by combining a water-insoluble plant protein (zein) and a hydrophilic polysaccharide (cellulose) through Schiff-base reaction. Zein assembles and precipitates into anisotropic particles after forming conjugates with cellulose. The wettability of conjugate particles at the interface can be precisely engineered by adjusting the ratio of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic components. The three-phase contact angle of a water droplet sitting on the substrate made of particles can be adjusted in a range from around 130°–40° when they are submerged in corn oil. The interfacial absorption kinetics of conjugate particles shows 2 to 4 times improvement than the particles made from sole material sources. The optimal polymer ratio is found to be 1:1.5 and 1:2 (zein:cellulose) for the corn oil-water system. In association with the enhanced interfacial affinity, emulsions stabilized by conjugate particles exhibit superior stability against droplet coalescence and bulk phase separation when going through the isoelectric point of the protein (around pH 6), high ionic strength, long-term storage, and thermal treatment. It has been found that 0.5 wt% conjugate particles are enough to stabilize emulsions containing more than 60 vt% oil.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108055
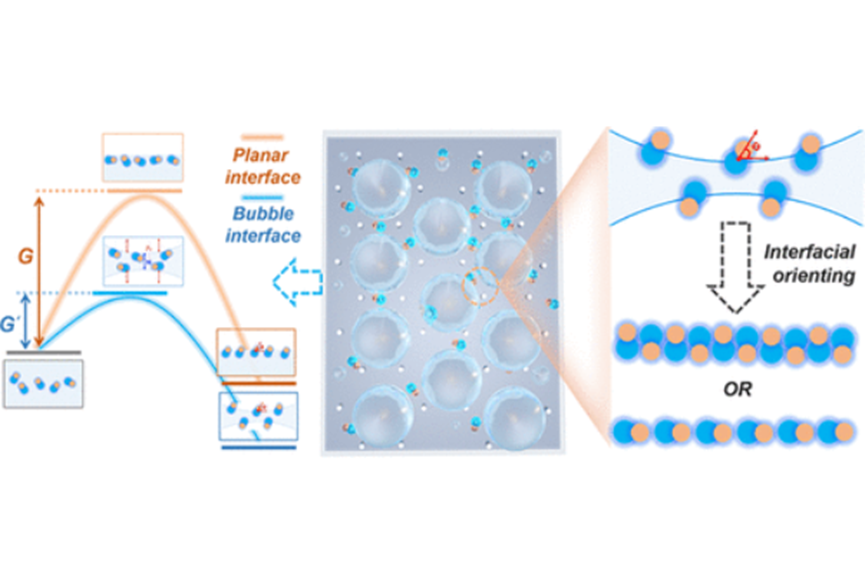
3. Gao, Jie; Sun, Dayin; Li, Zheng; Zhang, Zeying; Qu, Zhiyuan; Yun, Yang; Min, Fanyi; Lv, Wenkun; Guo, Mengmeng; Ye, Yilan; Yang, Zhenzhong*; Qiao, Yali*; Song, Yanlin*. Orientation-Controlled Ultralong Assembly of Janus Particles Induced by Bubble-Driven Instant Quasi-1D Interfaces, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(4): 2404–2413.
Constructing precisely oriented assemblies and exploring their orientation-dependent properties remain a challenge for Janus nanoparticles (JNPs) due to their asymmetric characteristics. Herein, we propose a bubble-driven instant quasi-1D interfacial strategy for the oriented assembly of JNP chains in a highly controllable manner. It is found that the rapid formation of templated bubbles can promote the interfacial orientation of JNPs kinetically, while the confined quasi-1D interface in the curved liquid bridge can constrain the disordered rotation of the particles, yielding well-oriented JNP chains in a long range. During the evaporation process, the interfacial orientation of the JNPs can be transferred to the assembled chains. By regulating the amphiphilicity of the JNPs, both heteraxial and coaxial JNP assemblies are obtained, which show different polarization dependences on light scattering, and the related colorimetric logic behaviors are demonstrated. This work demonstrates the great potential of patterned interfacial assembly with a manageable orientation and shows the broad prospect of asymmetric JNP assembly in constructing novel optoelectronic devices.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c11429
4. Tang, Zian; Qu, Kairu; Wen, Zhendong; Ye, Yilan; Sun, Dayin; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Supramolecular Nanofibers via Protrusion Budding Interfacial Membrane, Soft Matter, 2023, 19 (9): 1705-1708.
.
We proposed an approach to achieve the nanofibers or composite nanofibers with functional nanoparticles by protrusion of the budding interfacial membrane at an oil-water emulsion droplet stabilized with copolymers. The nanofibers are composed of wrapping monolayer of the copolymers, whose length is tunable with the copolymer concentration and water/oil ratio of the emulsion.

DOI:10.1039/d2sm01689c
5.Xu, Wei; Ye, Yilan; Sun, Dayin; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Single-chain nanoparticle catalyzed polymerization toward composite nanoparticles, J. Polym. Sci., 2023: 1–9.
Single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) as a confined space are promising tosynthesize structured nanoparticles. We report a facile synthesis of SCNPcolloidal initiators by loading reducing agents during the formation of theSCNPs and the application in redox freeradical polymerization to achievecomposite nanoparticles with tunable compositions and microstructures.The SCNP initiators could be large-scale achieved by electrostatic-mediatedintramolecular crosslinking polymers by metallic complexation with pro-tonated PVP at ambient temperature. The catalytic polymerization occursinwardly under facile conditions to large scale fabricate composite nanopar-ticles with tunable microstructures from core-shell to tadpole-shapes. Thefacile approach could be extended to derive functional composite nanopar-ticles by loading desired materials such as paramagnetic Fe3O4, catalytic Pt,and enzymes.
https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.20230379
Reviews
1.Yang, Jiye; Sun, Dayin; Wang, Yan; Gu, Anqi; Ye, Yilan; Ding, Shujiang; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Progresses in Template Synthesis and Applications of Hollow Materials, Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220665.
Hollow materials are emerging as functional materials with unique characteristics in tunable cavity, high specific active surface area and enhanced mass transfer. Janus hollow materials are readily derived upon spatial compartmentalization of multiple components thus functions. Template synthesis is highly efficient to synthesize the hollow materials with tunable microstructure and composition. In the first part of this review, recent advances in the template synthesis of the representative hollow materials are concisely summarized. In the second part, typical applications of the hollow materials in catalysis, energy storage, oil/water separation and drug delivery are introduced. This review will end with a perspective to call for more efforts in the development of new methods toward high performance hollow materials with tailored properties.
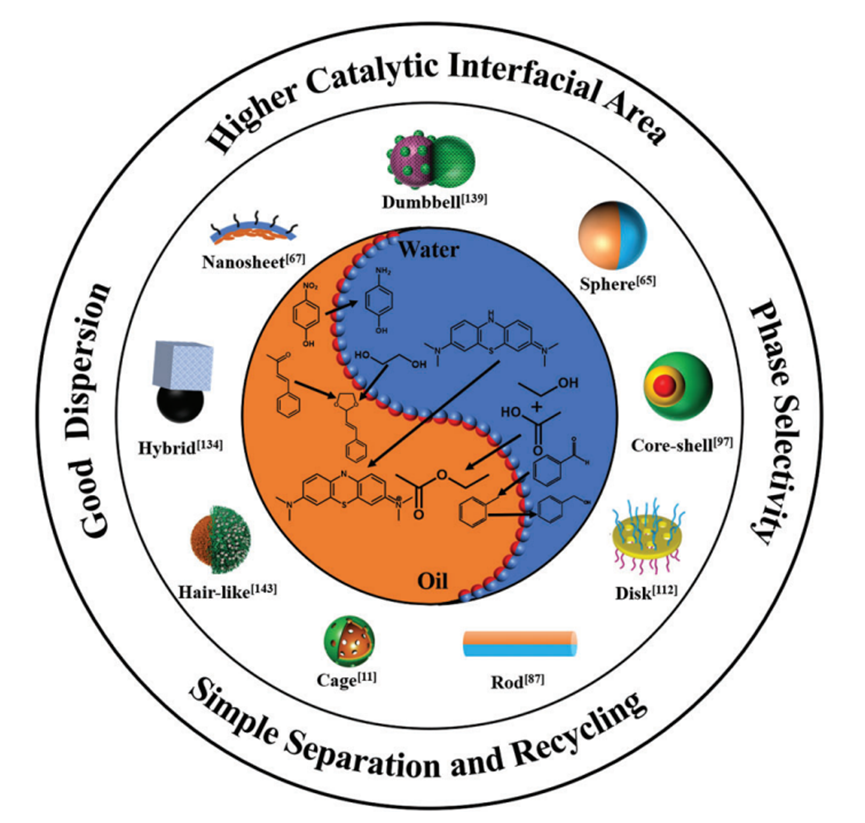
2. Chen, Chen; Zhang, Linlin*; Wang, Na; Sun, Dayin; Yang, Zhenzhong*. Janus Composite Particles and Interfacial Catalysis Thereby. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023: 2300280.
Janus composite particles (JPs) with distinct compartmentalization of varied components thus performances and anisotropic shape display a variety of properties and have demonstrated great potentials in diversify practical applications. Especially, the catalytic JPs are advantageous for multi-phase catalysis with much easier separation of products and recycling the catalysts. In the fifirst section of this review, typical methods to synthesize the JPs with varied morphologies are brieflfly surveyed in the category of polymeric, inorganic and polymer/inorganic composite. In the main section, recent progresses of the JPs in emulsion interfacial catalysis are summarized covering organic synthesis, hydrogenation, dye degradation, and environmental chemistry. The review will end by calling more efffforts toward precision synthesis of catalytic JPs at large scale to meet the stringent requirements in practical applications such as catalytic diagnosis and therapy by the functional JPs.